Locky ransomware was first detected in February 2016 and quickly became one of the year’s most significant cybersecurity threats. It was quickly recognized as a sophisticated and devastating form of malware.
This ransomware is believed to have been created by the Russian hacker group Evil Corp, which was also responsible for operating the Necurs botnet, a critical tool in distributing Locky and other malware.
This article explores Locky ransomware’s notable attacks, how it works, and what to do in case of a ransomware attack.
Locky ransomware primary targets and notable attacks
While Locky has affected organizations across various sectors, it has shown a particular focus on healthcare institutions. Hospitals were often targeted due to their critical need for immediate access to patient data and sometimes outdated cybersecurity practices.
One of the first major Locky attacks targeted Hollywood Presbyterian Medical Center in Los Angeles on February 18, 2016. The hospital paid a $17,000 ransom in Bitcoin to regain access to their systems. This high-profile incident brought ransomware into the public spotlight and sparked fears about the vulnerability of healthcare institutions to such attacks.
Variants and evolution
Locky ransomware is not active anymore, however, since its initial release,it has evolved with several variants, each using different file extensions for encrypted files:
- Original Locky (.locky)
- Zepto (.zepto)
- Odin (.odin)
- Thor (.thor)
- Aesir (.aesir)
- Osiris (.osiris)
- Diablo6 (.diablo6)
- Lukitus (.lukitus)
Each variant introduced minor changes to evade detection and improve the ransomware’s effectiveness.
How to identify Locky: main IOCs (Indicators of Compromise)
IOCs (Indicators of Compromise) are digital traces left by attackers during a cyberattack. These clues, like file extensions, file hashes, and IP addresses, help identify malware or malicious activity. Technical knowledge might be needed to locate some IOCs, or you can use a ransomware ID tool to search for the strain that infected your machine and network.
Here are the key characteristics and artifacts to identify Locky and recognize its main Indicators of Compromise (IOCs):
- Files suddenly become inaccessible
- File extensions changed to one of Locky’s variants (.locky; .zepto; .odin; .thor; .aesir; .osiris; .diablo6; .lukitus)
- Unusual network activity
- Appearance of ransom notes on the desktop or as text files in various directories
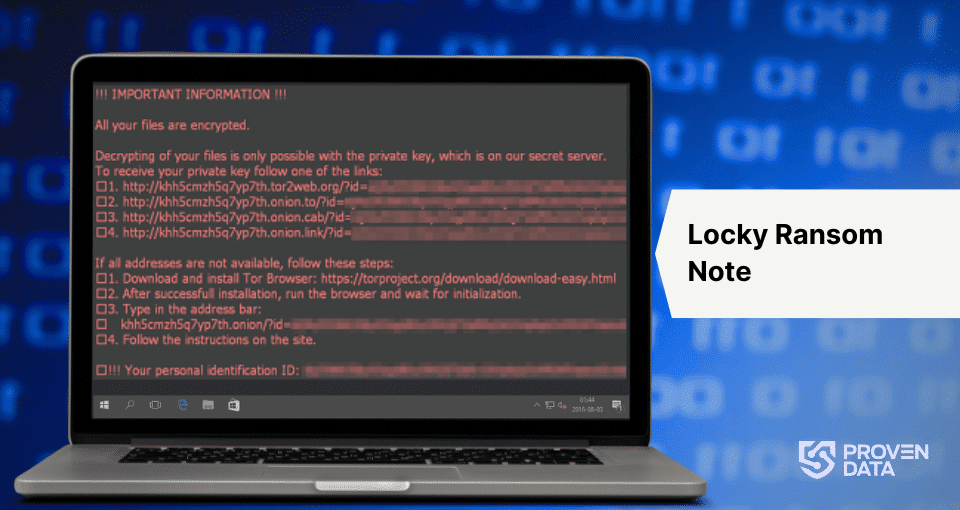
How Locky ransomware works
Understanding Locky’s ransomware tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) is crucial. Users can significantly improve their defenses against this sophisticated threat actor with this knowledge.
Locky ransomware typically follows these steps in its attack process:
1. Initial access
Locky is primarily spread through phishing emails containing malicious attachments, often disguised as invoices or other common business documents. The senders use Social Engineering to convince people to trust their emails and click or open attachments.
When the victim opens the attached document (usually a Microsoft Word file), they see gibberish text. However, this file contains malware that enables macros to trigger a malicious script that downloads and installs the Locky ransomware executable.
2. File encryption
Once installed, Locky encrypts files on the victim’s computer and any connected network drives. It targets a wide range of file types, including documents, images, and videos. Encrypted files are renamed with a unique 16-character combination and given a new extension.
Locky uses a combination of AES-128 and RSA-2048 encryption algorithms. The AES key is generated on the attacker’s server, making manual decryption nearly impossible.
3. Ransom demand
After encryption, Locky displays a ransom note on the victim’s desktop. This note instructs the user to download the Tor browser and visit a specific dark web site for payment instructions. The ransom demand typically ranges from 0.5 to 1 Bitcoin, with the exact amount varying over time as Bitcoin’s value fluctuates.
What to do in case of a Locky attack
When you realize Locky deployed its payload into your machines or network, you must stop using them and contact a ransomware recovery service provider.
These services can assist you with incident response and mitigation, minimize downtime, and provide data recovery if necessary. Requesting a digital forensics report is also recommended. This document can give you insights into how the attack happened and whether the threat actors left any backdoors they can use for a future attack.
Report the incident to the relevant authorities
Many jurisdictions have laws requiring reporting certain types of cyber incidents, especially those involving personal data breaches. Your report can also contribute to the broader understanding of the threat landscape, helping other organizations defend against similar attacks. In some cases, authorities may have information or tools that can assist in the recovery process.
Contact the Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT), US-CERT, and local and federal law enforcement agencies like the FBI. Provide as much detail as possible about the attack, including any indicators of compromise, the extent of the damage, and any evidence of data exfiltration. Be prepared to share system logs, network traffic data, and other relevant technical information.
Restore systems from clean, offline backups if available
Before beginning the restoration process, verify that your backups are clean and unaffected by the malware. Ensure that the underlying infrastructure is clean and secure. This may involve reimaging affected machines or, in severe cases, replacing hardware entirely.
Begin the restoration process, starting with critical systems and data. Prioritize based on business needs and dependencies between systems.
After restoration, thoroughly test each system to ensure it’s functioning correctly and shows no signs of infection.
Seek assistance from cybersecurity professionals
Engaging with ransomware recovery professionals is crucial in effectively responding to and recovering from a Locky attack. These experts bring specialized knowledge and tools that can significantly improve your response and recovery efforts. They can also help ensure that your response meets all relevant legal and regulatory requirements, particularly data protection and breach notification laws.
Cybersecurity professionals can help manage the incident response process, ensuring that all necessary steps are taken correctly and urgently. They can conduct a detailed forensic analysis of affected systems to determine the initial infection vector, the extent of the damage, and whether any data exfiltration occurred.
This information is crucial for understanding the full impact of the attack and preventing future incidents. Based on their findings, cybersecurity professionals can develop a comprehensive recovery strategy tailored to your organization’s specific situation and needs. By the end, they can provide recommendations for enhancing your security posture to prevent similar attacks in the future. This might include suggestions for improved network segmentation, enhanced monitoring capabilities, or additional security controls.
How to prevent Locky ransomware attacks
Proactive measures and continuous vigilance are key to maintaining robust cybersecurity defenses. Implementing strong access controls is a vital aspect of ransomware prevention. This includes applying the principle of least privilege, ensuring that users only have access to the resources necessary for their roles, thereby limiting the potential impact of a compromised account. Multi-factor authentication is also a prevention method that adds an extra layer of security, making it significantly more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access even if they obtain user credentials.
The final piece in ransomware prevention and mitigation is having a detailed Incident Response Retainer with a trusted provider, and developing a comprehensive incident response plan. This plan should outline detailed steps during a cyberattack and assign roles and responsibilities to team members. Regular testing and updating of this plan through tabletop exercises ensure that the organization is prepared to respond swiftly and effectively in case of an attack.