The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of interconnected physical devices embedded with sensors and software that enable them to collect and exchange data over the Internet. This facilitates communication and automation without human intervention. The increasing adoption of IoT devices in business environments has created new opportunities for efficiency and innovation. However, it has also introduced significant security challenges that organizations must address.
Businesses and organizations must protect IoT-connected devices with the best cyber security practices, mainly because, unfortunately, many companies will face cyber threats at some moment. The average data breach cost in 2024 was nearly $5 million, and 74% of the targeted companies were small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs).
What is IoT security?
Internet of Things (IoT) security encompasses the technologies and practices designed to protect interconnected devices and networks from unauthorized access and cyber-attacks. As businesses integrate more smart devices into their operations, from security cameras to industrial sensors, robust security measures become increasingly critical.

Why IoT security matters for your business
Cybercrime is expanding at an alarming rate. Criminal gangs quickly become fully operational organizations with specialized labor helping them infiltrate networks. Many cybercriminals take advantage of organizations’ weak security, known as vulnerabilities, within networks, systems, and endpoint devices.
The consequences of inadequate IoT security can be severe:
Financial impact: Organizations face significant costs from data breaches, system downtime, and recovery efforts.
Data vulnerability: IoT devices collect and transmit sensitive information, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals. Our digital forensics team can help assess your data security vulnerabilities and identify methods to eliminate them.
Operational disruption: A compromised IoT device can be an entry point to your entire network, potentially disrupting critical business operations.
Example of IoT attack
In 2010, researchers discovered that the Stuxnet virus had been used to physically damage Iranian centrifuges. The attacks, which began in 2006 and peaked in 2009, specifically targeted supervisory control and data acquisition systems in industrial control systems. The virus used malware to corrupt instructions sent by programmable logic controllers.
This attack opened the door for subsequent industrial network breaches, as demonstrated by malware variants like CrashOverride (also known as Industroyer) and Triton.
The threat to consumer IoT devices became particularly evident in 2016 with the emergence of the Mirai botnet, one of the largest IoT-based attacks to date. The botnet first targeted journalist Brian Krebs’ website and French web host OVH in September of that year, generating attacks of unprecedented scale at 630 gigabits per second and 1.1 terabits per second, respectively. The following month, the botnet struck domain name system service provider Dyn’s network, causing widespread disruption to major websites, including Amazon, Netflix, Twitter, and The New York Times. These attacks were particularly alarming because they were executed through typical consumer IoT devices, such as IP cameras and routers, demonstrating how everyday smart devices could be weaponized for large-scale cyber attacks.
Steps to protect IoT devices
Make it a personal and business habit to protect the Internet of Things with better cyber security. As your business grows (both in size and dependence on technology), creating a cyber security plan that will scale with the company is key. If your organization takes connected device security seriously, it can adopt this new expectation as a mandatory practice.
This can be achieved through a comprehensive approach in:
- Employee security best practices awareness training program
- Cybersecurity incident response plan
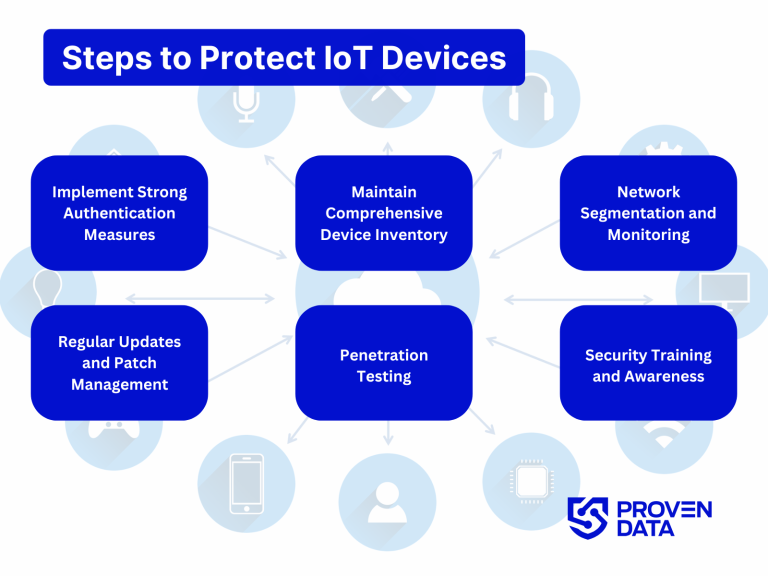
1. Implement strong authentication measures
Start with robust password policies and multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all IoT devices. Create unique, complex passwords and change them regularly. For additional security, consider implementing certificate-based authentication.
2. Maintain comprehensive device inventory
Develop and maintain a complete inventory of all IoT devices connected to your network. This includes:
- Device identification and location
- Purpose and criticality
- Security configurations
- Update and patch status
3. Network segmentation and monitoring
Create separate network segments for IoT devices to limit potential damage from security breaches:
- Isolate IoT devices from critical systems
- Implement firewalls between network segments
- Monitor network traffic for suspicious activities
- Regular security audits and assessments
4. Regular updates and patch management
Establish a systematic approach to device maintenance:
- Schedule regular firmware updates
- Apply security patches promptly
- Document all update procedures
- Test updates before deployment
5. Penetration testing
Regular penetration testing helps identify vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Consider working with security experts to:
- Assess device vulnerabilities
- Test network security
- Evaluate authentication mechanisms
- Review security policies and procedures
6. Security training and awareness
Develop comprehensive training programs for employees:
- IoT security best practices
- Device handling procedures
- Incident response protocols
- Security policy compliance
Common IoT security vulnerabilities
A security vulnerability is a weakness in a system, software, or hardware that attackers can exploit to compromise the system’s confidentiality, integrity, or availability. Addressing these vulnerabilities is crucial because unpatched vulnerabilities act as open doors for cybercriminals, potentially leading to significant data breaches, financial losses, and damage to an organization’s reputation.
Default credentials and weak authentication. Many IoT devices have factory-set passwords that are easily discoverable. The devices are exposed to unauthorized access if these credentials are not changed.
Limited built-in security. Most IoT devices have minimal security features due to hardware constraints, making them more susceptible to attacks. Discover how IoT forensics can help identify vulnerabilities.
Network vulnerabilities. Unsecured network connections can expose IoT devices to various cyber threats.
Internet of Things devices in business
Now more than ever, businesses of all sizes use technology to streamline processes and improve their operations. Even the smallest of small businesses use technology (computers, servers, data storage) to modernize their company activity. Each additional connected device can pose a security risk or create an opportunity for the business to strengthen its cyber security framework.
Industries and sectors of all kinds are adopting IoT devices:
- Industrial machinery: manufacturing automation such as robotics and machine-driven production
- Connected markets: real-time information relating to marketplace information
- Fleet and logistics: ships, vehicles, aircraft & machines that use data for managing
- Consumer products: appliances, home assistants, security cameras, etc.
If your company uses, internet-connected machinery and a cyber attack occurs, every second counts when products can’t be manufactured and orders cannot be fulfilled.
Protect the IoT by taking action today
Proven Data is here to assist businesses who wish to take their data security seriously and protect the Internet of Things against cyber attacks such as ransomware. Our cyber security professionals have the experience to evaluate your company’s needs and provide cyber security solutions.