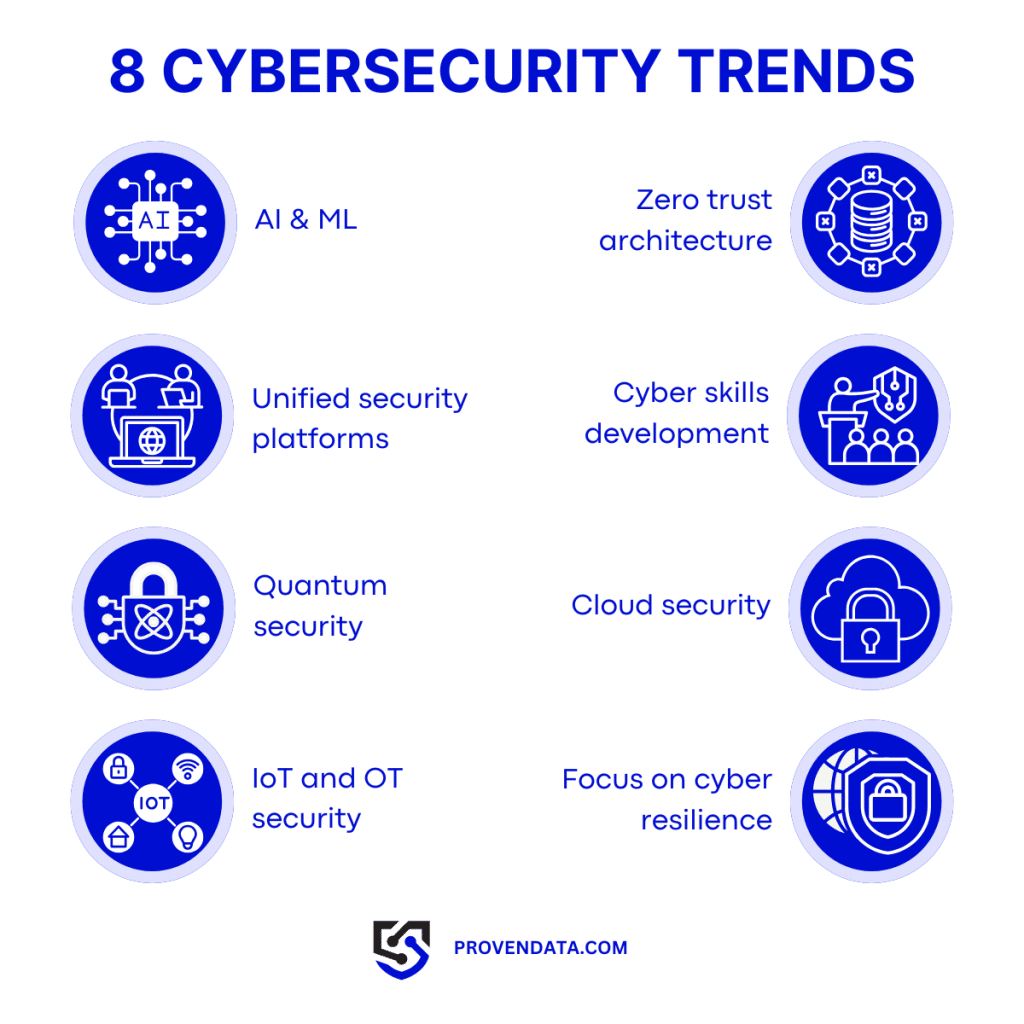
Cybersecurity has become a cornerstone of business operations, government functions, and personal privacy. It encompasses protecting digital assets, operational technology (OT), and human safety in an increasingly interconnected world. In 2025, the cybersecurity landscape is expected to undergo significant transformations, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and cybercriminals’ increasing sophistication.
According to recent studies, 72% of organizations report increased cyber risks over the past 12 months, with 63% citing the complex and evolving threat landscape as their greatest challenge to achieving cyber resilience.
The vulnerability of critical infrastructure remains a focal point for nation-state attackers in 2025:
- Healthcare systems face heightened targeting, as evidenced by attacks on United Healthcare and Ascension Health.
- Power plants, water facilities, and transportation systems require enhanced protection.
- Increased focus on OT security.
This comprehensive guide explores the most significant cybersecurity trends and provides actionable strategies for building cyber resilience in 2025.
1. AI as a double-edged sword in cybersecurity
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are double-edged swords in cybersecurity. On the one hand, they empower organizations to detect and respond to threats in real-time by analyzing vast amounts of data and identifying patterns that humans might miss. On the other hand, cybercriminals are also leveraging AI to develop more sophisticated attacks, such as AI-generated phishing emails and malware that adapts to evade detection.
In 2025, AI-driven security tools will become indispensable for threat hunting, anomaly detection, and automated incident response.
Key developments include:
- AI-powered defense mechanisms for quick threat detection and response
- AI-enabled threat intelligence analysis and pattern recognition
- Enhanced incident response through AI automation
- Increased sophistication of AI-powered attacks
2. Zero trust architecture
The traditional “trust but verify” approach is no longer sufficient. Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify,” ensuring that no user or device is trusted by default, even within the network.
By 2025, Zero Trust will become the gold standard for network security frameworks, particularly for organizations with hybrid work environments and cloud-based infrastructures.
Key strategies:
- Implement granular access controls and continuous authentication.
- Adopt network micro-segmentation to limit lateral movement by attackers.
- Ensure visibility into all network activities and enforce strict identity verification.
3. Unified security platforms and vendor consolidation
The trend toward consolidated security solutions is accelerating in 2025. Organizations are moving from fragmented, multi-vendor architectures to integrated, AI-driven platforms to reduce complexity and improve efficiency. This approach emphasizes reducing the mean time to detect (MTTD) and mean time to respond (MTTR). Research shows that 45% of organizations will use fewer than 15 cybersecurity tools by 2028.
Benefits of consolidation include:
- Improved visibility and efficiency.
- Optimized resource utilization.
- Enhanced AI-powered analysis capabilities.
- Reduced complexity in security operations.
4. Cyber skills development
The cybersecurity sector faces a critical workforce shortage, with estimates ranging from 2.8 to 4.8 million unfilled positions globally. Only 14% of organizations report having the necessary talent, while 49% of public-sector organizations lack an adequate cybersecurity workforce.
Organizations must invest in personnel training and hiring experts to counterstrike the increased sophistication of cyber attack methods. Studies show that 68% of organizations focus on upskilling current employees, and 24% promote apprenticeship programs.
Benefits of cybersecurity training:
- Create a cybersecurity awareness culture
- Prevent social engineering and phishing attacks
Protects against unintentional insider threats
5. Quantum security
Quantum computing promises to revolutionize industries by solving complex problems at unprecedented speeds. However, it also poses a significant threat to traditional encryption methods. Quantum computers could break widely used encryption algorithms, such as RSA and ECC, rendering current security measures obsolete.
While practical quantum attacks aren’t yet feasible, organizations must prepare for future threats by taking proactive steps to understand quantum threats and implement quantum-resistant defenses.
Key actions:
- Transition to post-quantum cryptography (PQC) standards.
- Address “Harvest Now, Decrypt Later” attacks, in which attackers collect encrypted data and decrypt it once quantum computing becomes viable.
- Implementation of quantum-resistant defenses
6. Increased focus on cloud security
The shift to cloud computing has accelerated, driven by the need for scalability and remote work capabilities. However, this has also expanded the attack surface, making cloud environments a prime target for cybercriminals. It’s vital that companies carefully choose their vendors and apply a multi-cloud approach.
Cloud security will be a top priority for organizations in 2025.
Key focus areas include:
- Securing multi-cloud environments.
- Implementing robust identity and access management (IAM).
- Ensuring compliance with shared responsibility models.
7. Expansion of IoT and OT security
The Internet of Things (IoT) and Operational Technology (OT) are transforming industries, from healthcare to manufacturing. However, many IoT and OT devices lack built-in security features, making them vulnerable to attacks.
In 2025, the proliferation of connected devices will necessitate stronger security measures, such as device authentication, encryption, and regular firmware updates. Governments and industries will also collaborate to establish security standards for IoT and OT devices.
Key strategies:
- Implement device authentication and encryption.
- Conduct regular firmware updates and vulnerability assessments.
- Establish visibility into IoT and OT ecosystems.
8. Focus on cyber resilience
In an era of persistent cyber threats, organizations are shifting their focus from prevention to resilience. Cyber resilience involves defending against attacks and ensuring the ability to recover quickly and maintain operations during and after an incident. Organizations must adopt holistic cyber resilience strategies in 2025 to face cyber attacks, including incident response planning, disaster recovery, and continuous monitoring.
Key actions:
- Develop comprehensive incident response plans.
- Conduct regular security assessments and penetration testing.
- Invest in AI-powered threat detection and response tools.
Conclusion
As we move through 2025, organizations must adapt to an increasingly complex cyber threat landscape. Success requires a holistic approach that combines technological innovation, workforce development, and strategic planning. By understanding and preparing for these trends, organizations can build the resilience needed to protect their assets and maintain operational continuity in an evolving digital world.