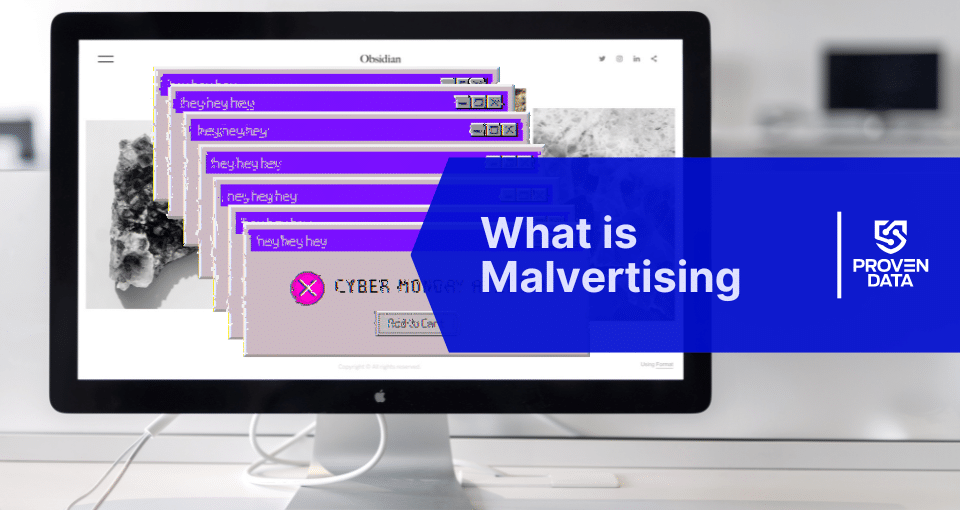
Malvertising, short for malicious advertising, is a cybersecurity threat that has become increasingly prevalent in the digital age. Cybercriminals use this technique to inject malicious code into legitimate online advertisements. These infected ads are then distributed through reputable ad networks and displayed on trusted websites, potentially exposing millions of users to malware, ransomware, and other cyber threats.
How does malvertising work?
Malvertising takes advantage of the complex ecosystem of online advertising. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the process:
- Attackers create malicious ads or inject malicious code into existing ads
- These ads are submitted to legitimate ad networks
- Ad networks, often unable to detect the malicious content, distribute the ads to various websites
- Users visiting these websites are exposed to malicious ads
- The malicious code may execute automatically (in a “drive-by download”) or when a user clicks on the ad
How to get rid of malvertising
If you suspect your device has been affected by malvertising, take the following steps:
- Disconnect from the internet to prevent further damage or data theft.
- Run a full system scan using up-to-date antivirus software.
- Remove any suspicious programs or browser extensions.
- Clear your browser cache and cookies.
- Update your operating system and all software to the latest versions.
- Change passwords for important accounts, especially if you suspect they may have been compromised.
The most effective way to remove malware and prevent new attacks is to contact professionals who can restore your system to its normal state and provide a forensics report. This report can inform you of how the hack happened and help you take steps to prevent it from happening again.
How to protect yourself from malvertising
Prevention is critical when it comes to malvertising. Here are some strategies to help protect yourself:
- Use ad blockers: Install reputable ad-blocking extensions in your browsers to reduce exposure to potentially malicious ads.
- Keep software updated: Regularly update your operating system, browsers, and plugins to patch known vulnerabilities.
- Enable click-to-play for plugins: This prevents automatic execution of content like Flash or Java, often exploited in malvertising attacks.
- Use robust antivirus software: Install and maintain up-to-date antivirus software with real-time protection.
- Be cautious with clicks: Avoid clicking on suspicious or too-good-to-be-true advertisements.
- Use a virtual private network (VPN): A VPN can provide an additional layer of security when browsing online.
- Implement network-level protection: For businesses, consider using network-level ad blockers and security solutions. You must remember that this is a security measure and not a prevention since VPN can’t protect you from cyber attacks if you eventually click on compromised links.
- Educate yourself and others: Stay informed about the latest cybersecurity threats and share this knowledge with friends, family, and colleagues. Knowing about potential dangers is the best way to prevent cybercriminals from succeed their attacks against you.
Examples of malvertising
Malvertising has affected even the most reputable websites and platforms. Here are some notable examples:
- In 2016, a malvertising campaign targeted users of popular adult websites, potentially exposing millions to ransomware.
- In 2011, Spotify fell victim to a malvertising attack that served malicious ads to users of its free version, potentially exposing them to malware.
- In 2013, a major malvertising attack on Yahoo.com put a significant number of the webpage’s 6.9 billion monthly visitors at risk. The attack infected users’ machines with the CryptoWall ransomware.
These examples demonstrate that malvertising can impact users across various platforms and even on trusted, high-traffic websites.
Risks of malvertising
The risks associated with malvertising are diverse and severe, ranging from direct financial losses to long-term privacy and security implications. Understanding these risks is crucial for internet users, businesses, and cybersecurity professionals alike in developing effective strategies to combat this pervasive threat.
One of the primary dangers is malware infection. Malicious advertisements can serve as vectors for delivering a wide array of malicious software to your device, including viruses, trojans, and spyware. These malicious programs can damage your system, compromise your files, and even give attackers remote access to your device.
Data theft is another severe risk associated with malvertising. Cybercriminals often design malvertising campaigns with the explicit goal of stealing sensitive information from unsuspecting users. This can include login credentials for various accounts, financial data such as credit card numbers or banking information, and personal identifiable information that could be used for identity theft. The stolen data may then be sold on the dark web or used directly by the attackers for further malicious activities.
Ransomware attacks have become increasingly prevalent in recent years, and malvertising is an effective distribution method for this type of malware. When a user’s device is infected with ransomware through a malicious advertisement, their files are encrypted, rendering them inaccessible. The attacker then demands a ransom payment, often in cryptocurrency, in exchange for the decryption key. This can lead to significant financial losses and data loss if the victim doesn’t have proper backups.
Financial fraud is yet another risk associated with malvertising. Attackers may use deceptive ads to trick users into directly providing financial information. These ads mimic legitimate banking sites or online stores, prompting users to enter their credit card details or other financial data. Alternatively, malvertising can lead users to fraudulent websites that process unauthorized transactions, resulting in direct economic losses.
When malicious code gains unauthorized access to a user’s device through an infected ad, it can compromise the user’s privacy in numerous ways. This may include monitoring browsing habits, accessing personal files and photos, or activating the device’s camera or microphone without the user’s knowledge. Such invasions of privacy can have far-reaching consequences, potentially exposing sensitive personal information or being used for blackmail.
Moreover, malvertising can lead to reputational damage for websites and businesses that unknowingly display these malicious ads. Users may lose trust in platforms that expose them to security risks, even if the platform itself was not directly responsible for the malicious content. This highlights the far-reaching impact of malvertising, affecting individual users and the broader digital ecosystem.