Ransomware and malware are types of cyberattacks that aim to disrupt business operations and monetary gain. Therefore, it is crucial to take preventive measures and to understand these threats to be safe online and ensure business continuity.
In this guide, you can check the differences and similarities between these two cyber threats, as well as how to keep your devices protected against them. Plus, what to do in case you suffer a malware or ransomware attack.
What is Malware
Malware, short for malicious software, is a broad term encompassing various types of harmful software designed to compromise computer systems, networks, and devices.
They are created by cybercriminals with the intent to cause damage, steal sensitive information, disrupt operations, or gain unauthorized access to systems.
Common types of malware
As an umbrella term, malware includes many types of attack techniques. Ransomware is the most destructive malware type and always has monetary gain as the goal.
Other types of malware can focus on different goals, such as business disruption or espionage.
Viruses
A virus is a malicious code or programs that infect other files and cause damage to the system. They can corrupt data, disrupt system functionality, and replicate themselves.
When the infected program or file is executed, the virus activates and spreads to other files or systems.
Trojan Horses
A trojan is a type of software that disguises itself as legitimate applications or files to deceive users into downloading and executing it. Unlike viruses, they don’t self-replicate.
They can steal sensitive information, create backdoors for attackers, or perform other harmful actions.
Spyware
Spyware is software that secretly collects information about a user’s activities and sends it to a third party. It secretly monitors a user’s activities without their knowledge or consent. This can include monitoring keystrokes, capturing screenshots, or using the computer’s camera.
Adware
Adware is malicious software that displays unwanted advertisements on a user’s device. It can be intrusive and may collect personal information for malicious purposes.
Adware often comes bundled with free software or browser extensions. It generates revenue for developers by showing ads, but some aggressive adware can negatively impact system performance.
Ransomware
Ransomware is a specific type of malware that encrypts a user’s files or systems, demanding a ransom for their release. It spreads rapidly and can cause significant damage to individuals, businesses, and critical infrastructure.
What is Ransomware
Ransomware is a specific type of malware that restricts access to data until a ransom is paid. Cybercriminals use multiple tactics to infect computers, devices, and networks with their encrypting algorithms, often starting through phishing emails that contain malicious links or attachments.
Once installed, ransomware uses a process called encryption to lock the victim’s files or entire systems. This transforms the data into an unreadable format, and only the cybercriminal possesses the decryption key needed to revert the files to their original state.
Ransomware threats range from restraining the decryption key to leaking the stolen data, and a successful attack can have severe consequences. Victims may experience the inaccessibility of critical data, disruption of business or organizational operations, financial losses associated with downtime, and potential reputational harm.
A recent example of a Ransomware attack
In November 2023, Toyota Financial Services Europe & Africa, a subsidiary of Toyota Motor Corporation, fell victim to a targeted cyberattack by the notorious Medusa ransomware group. Despite the severity of the attack, Toyota took a firm stance against the ransom demand of $8 million.
The attack resulted in the leakage of sensitive and financial information. Among the data compromised were customers’ full names, addresses, lease-purchase information, and contact details.
The company took a risk that the FBI and CISA advise doing since complying with cybercriminals can lead to financing terrorist attacks among other criminals that go beyond the cyber sphere.
Common types of ransomware
Despite being a unique type of cyberattack, ransomware has several types of techniques and methods, including a business model.
Here are the common types of ransomware:
Crypto ransomware
Crypto ransomware is the traditional attack method: it encrypts files on a victim’s system, making them inaccessible without a decryption key.
Threat actors display a ransom note, demanding payment in cryptocurrency (e.g., Bitcoin) for the decryption key.
A crypto ransomware results in severe data loss, financial losses, and operational disruptions.
Lockers
Lockers take control of the victim’s entire system, locking them out completely. Victims cannot access any files, applications, or system functions. It displays a full-screen message (lock screen) demanding payment.
The impact of locker ransomware is a complete system lockdown, disrupting work and productivity.
Leakware
Leakware, also known as doxware, threatens to leak sensitive data unless a ransom is paid. Instead of encrypting files, it exfiltrates sensitive data (personal, financial, or corporate). The attacker threatens to publish the data publicly unless the victim pays.
These attacks lead to reputation damage, legal consequences, and potential financial losses.
Most recent ransomware attacks apply double extortion techniques where the criminals not only encrypt the data but also threaten to leak stolen information.
Ransomware as a Service (RaaS)
RaaS is a criminal business model where developers create and distribute ransomware. Aspiring attackers can rent or purchase ransomware kits from RaaS providers. These kits include the ransomware code, infrastructure, and payment mechanisms, i.e., there is no need to understand algorithms to perform a ransomware attack.
The RaaS model allows ransomware attacks to be more common, leading to growing cyberattack groups with multiple goals, despite the monetary gain.
What is the difference between malware and ransomware
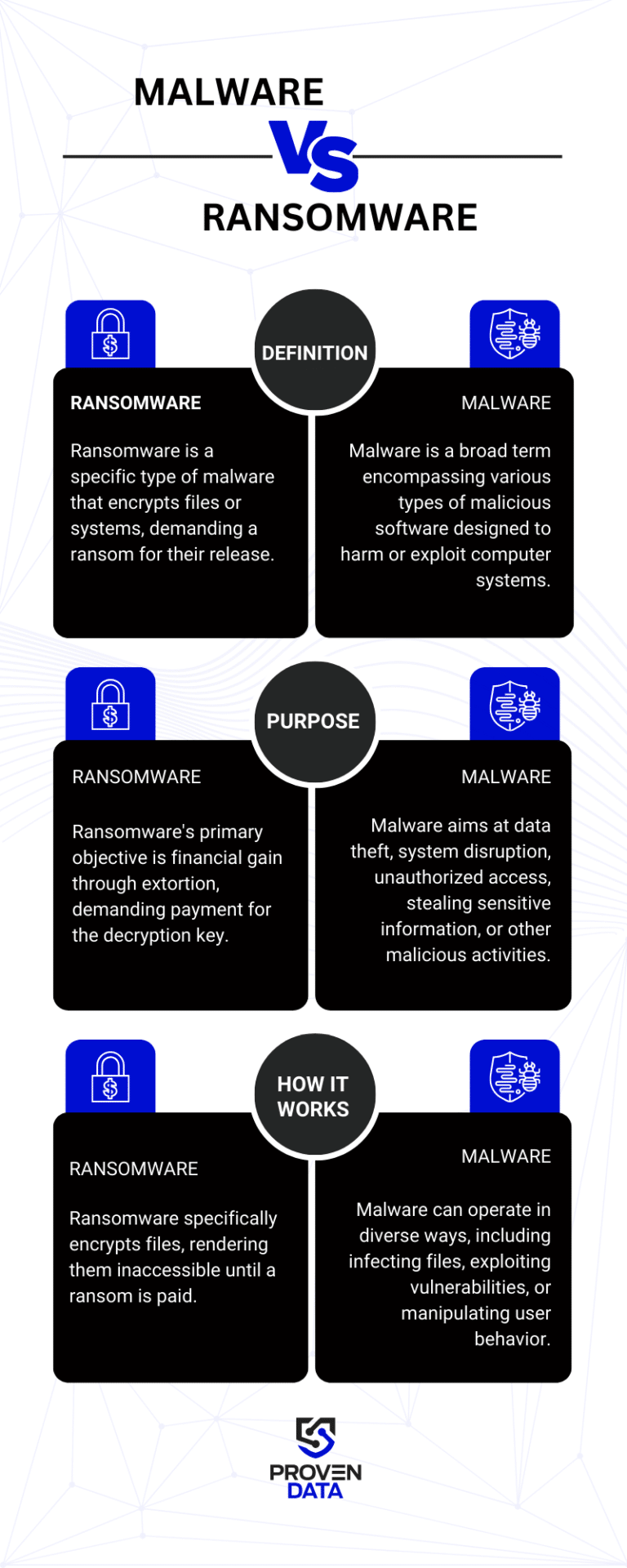
The main difference between ransomware and malware is that while ransomware is a specific type of cyberattack, malware is an umbrella term for several types of attacks.
Malware’s general purpose is to disrupt business services or cause data loss. Ransomware adds to this data encryption and ransom payment, showing their monetary motivation.
How to prevent malware and ransomware
By preventing cyberattacks, such as malware and ransomware, businesses and individuals alike can ensure data privacy. For individuals, it means they can decrease successful online scams and protect their personal information, such as social security numbers and banking information. For businesses, preventive and security measures not only ensure data security but also keep them compliant with data privacy laws and requirements.
Keep software updated
Regularly updating your operating system and software applications is crucial for maintaining a secure digital environment. Updates often include patches that address newly discovered vulnerabilities, preventing exploitation by cybercriminals.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring additional authentication steps beyond just entering a password. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if a password is compromised.
Educate employees
Regular cybersecurity awareness training empowers employees to recognize and avoid potential threats. This includes identifying phishing emails, avoiding suspicious links, and understanding best practices for online security.
What to do in case of a malware or ransomware attack
In the event of a malware or ransomware attack, notify your organization’s IT support or security team immediately. Provide details about the incident, including any observed symptoms, to enable them to assess the situation and take necessary actions.
The information you provide is essential to understand the infection and to identify the ransomware strain in your network.
If your organization has an incident response plan, follow the predefined procedures outlined in the plan. This may include specific steps for identifying, containing, eradicating, recovering, and investigating the incident.
Contact cybersecurity service
The best course of action to take after a ransomware attack is to contact a cybersecurity and ransomware removal service.
These services will provide you with every step of incident response and mitigation. From identifying and containing, to removing the malware from your computer or network and contacting authorities. Also, experts can recover lost, encrypted, or corrupted data, being the best option for victims to remediate attacks and salvage their businesses’ future.
Contact Proven Data experts 24/7 for emergency ransomware removal and data recovery services.